Welcome back to our 2nd installment of Sustainability 101, an educational partnership with The Sustainable Mag, a digital magazine about sustainability started by a SUMAS student and alumnus. Every month, we post an interesting topic related to sustainability, with the aim of educating around this important subject. If you missed part one, you can read it here. This month we’re tackling the definition and importance of social inclusion, why it is important, and how it relates to sustainability.
What defines social inclusion?
According to the United Nations “Social inclusion is defined as the process of improving the terms of participation in society, particularly for people who are disadvantaged, through enhancing opportunities, access to resources, voice and respect for rights.”
To understand social inclusion, it is important to note that “exclusion occurs because certain groups are systematically disadvantaged and/ or discriminated against on the basis of their identity: ethnicity, race, religion, sexual orientation, caste, descent, gender, age, disability, HIV status, migrant status or where they live. Therefore, exclusion can occur linked to multiple dimensions of one person’s identity.“ (shareweb.ch)
Importantly, the UN points out that social inclusion is multidimensional, and is not only limited to material wealth. Below is an example of some of the facets of social inclusion:
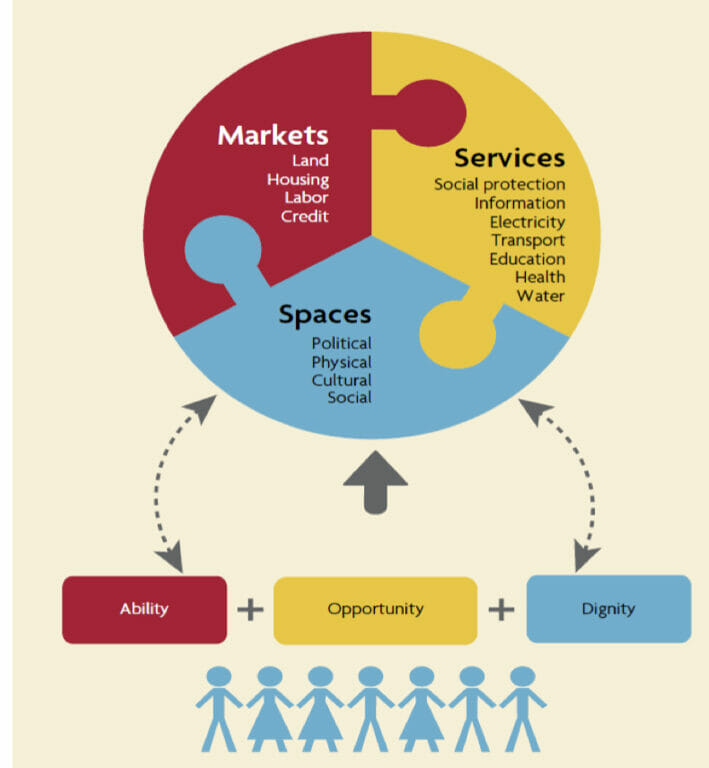
(Source: World Bank)
Why is it so important?
Besides the fact that by being socially included, people achieve higher levels of wellbeing and happiness, social inclusion also leads to less conflict and can positively impact the economy.
Social inclusion and sustainability
In our first installment of sustainability 101, we discussed how “solving social and environmental issues can lead to a liveable planet, poverty reduction, and economic resilience too.” As such, social inclusion is an essential cornerstone of sustainability and sustainable development.
How do we achieve this?
According to the Western Australia Council of Social Services “Social sustainability occurs when the formal and informal processes; systems; structures; and relationships actively support the capacity of current and future generations to create healthy and livable communities. Socially sustainable communities are equitable, diverse, connected, and democratic and provide a good quality of life.”
But as the World Bank points out: “Unless the root causes of structural exclusion and discrimination are addressed, it will be challenging to support sustainable inclusive growth and rapid poverty reduction.”
Language matters
As we aim to achieve social inclusion, it is important to consider the inclusivity of our language. For example, even in the above definition of social inclusion by the UN, the use of the word “disadvantaged” can itself be considered non-inclusive.

(Source: Educational Influencer and Historian, @BlairImani)
People who have been historically categorized as being disadvantaged or underprivileged have in fact been intentionally excluded and deprived of economic, and/or other, opportunities. Being intentional with our words, rather than making blanket statements about entire communities can do a lot of services. Instead of saying disadvantaged, marginalized, or underprivileged, be specific. Are you talking about black people? Are you talking about queer people? Are you talking about poor, working-class people? Are you talking about a community that has been under-served, historically oppressed, and underrepresented? Say that instead.
We hope you’re enjoying learning about the different elements of sustainability with us on Sustainability 101.
Next up: What is intersectionality?

